PTFE Injection Molding

What is PTFE Injection Moulding?
PTFE injection molding, also referred to as injection moulding PTFE, is a specialized process used to shape Teflon (PTFE) into high-performance parts that require exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
- The PTFE moulding process begins with precision mold design and pre-processing of PTFE resin
- Due to its high melt viscosity, traditional injection molding is modified or replaced with paste extrusion and sintering techniques
- Post-molding sintering is essential to ensure strength and molecular integrity
- Final parts may be fine-tuned with machining, surface treatments, or coatings
As experts in molding PTFE, we provide tailored PTFE Molding solutions for industries operating in chemically aggressive or high-temperature environments.
Injection Molding PTFE Parameters Table
| Parameter | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | 3.0mm - 10.0mm |
| Maximum Part Size | 200mm x 200mm x 100mm |
| Minimum Feature Size | 0.5mm - 1.0mm |
| Tolerances | ±0.1mm - ±0.5mm |
PTFE Material Properties
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance fluoropolymer ideal for injection molded PTFE parts due to its key Material Properties:
- Superior chemical resistance – inert to nearly all corrosive substances
- Excellent thermal endurance – continuous operation up to 260°C
- Extremely low friction – ideal for Teflon moulding process applications
- Non-stick, non-wetting surface – prevents fouling and contamination
- Great dielectric properties – preferred in insulation and high-voltage systems
| Property | Density | Tensile Strength | Flexural Strength | Impact Strength (Unnotched) | Heat Deflection Temp (0.45 MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value/Description | 2.14 - 2.20g/cm³ | 20 - 35 MPa | 14 - 20 MPa | 5 -12 kJ/m² | 120 - 130℃ |
- The above parameters represent the baseline performance of the materials. Actual application should be dynamically optimized based on specific working conditions.
Related Process
Looking for High-Performance PTFE Molding?
Advantages & Disadvantages of PTFE Injection Molding
Advantages
- Resistant to virtually all chemicals – key strength of PTFE injection moulding
- Extreme temperature resistance – maintains properties in harsh heat conditions
- Low friction – reduces wear in moving parts, ideal for molding PTFE bearings and seals
- Electrical insulation – excellent for sensitive electronic components
- Non-stick surface – prevents material buildup in Teflon moulding process
Disadvantages
- High shrinkage and difficulty in processing – challenges in injection moulding PTFE
- Requires post-molding sintering – adds time and complexity
- Limited adhesion – overmolding or bonding to other materials requires special treatments
- Higher cost compared to standard plastics
Applications of Injection Molding PTFE
Medical Industry
- Sterile labware
- Non-stick surgical components
- PTFE moulding for seals and valves
- Anti-corrosive medical enclosures
Aerospace & Defense
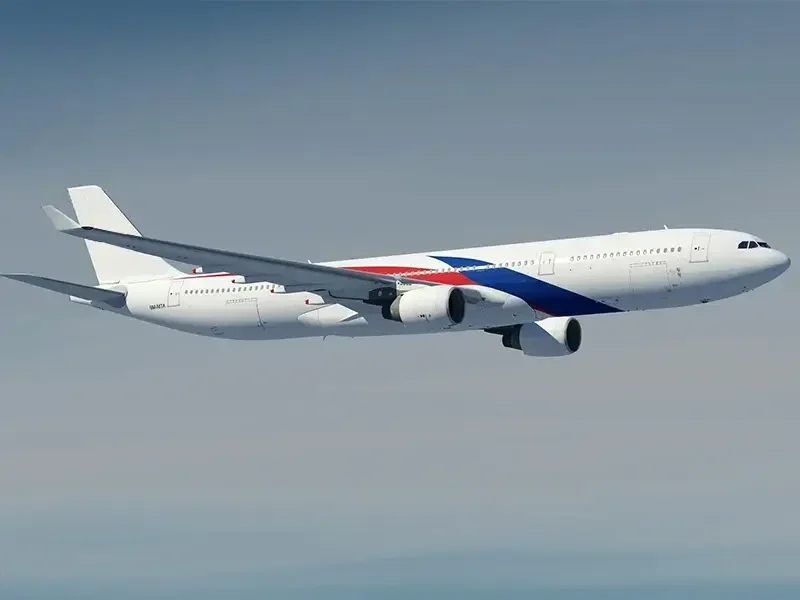

- Thermal insulators and guides
- Fuel system seals
- Cable insulations
- Chemically stable connectors
Electronics & Semi
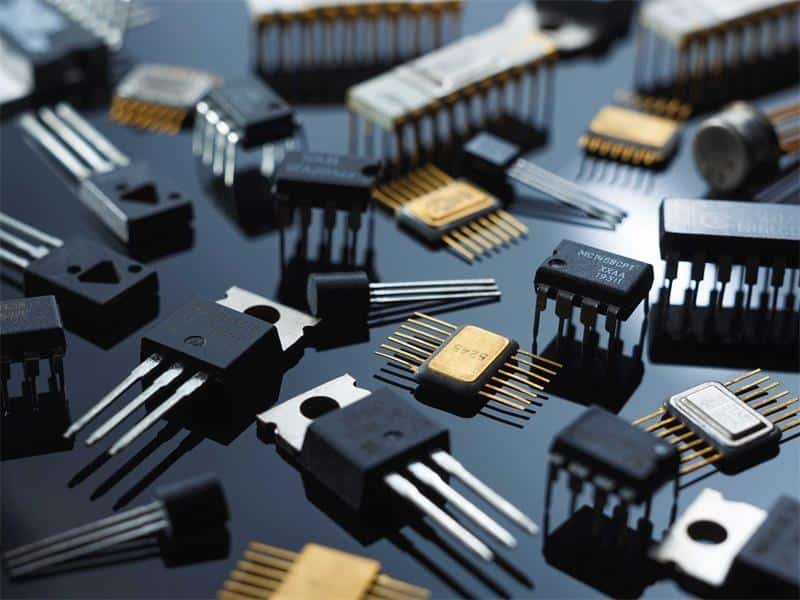

- High-voltage insulation
- Non-conductive fittings
- Wafer processing components
- PCB supports
Industrial Applications
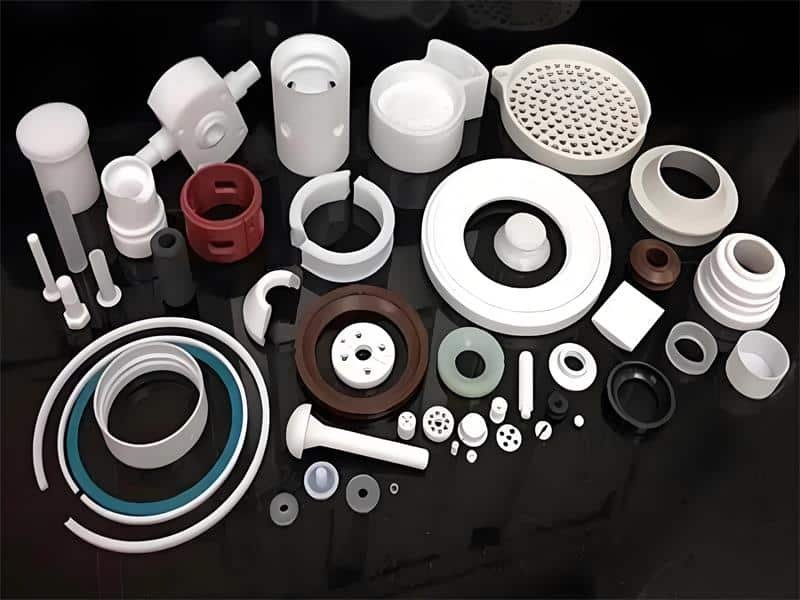

- Pumps, gaskets, and valve linings
- Low-friction slides
- Teflon moulding parts for chemical tanks
- Anti-adhesive machine components
Jiangzhi PTFE Injection Molding Parts are Guaranteed
100% Satisfaction – High-performance, injection molded PTFE parts with superior heat and chemical resistance. Your requirements, precisely delivered through expert PTFE moulding.

FAQs About Injection PTFE Molding
Purpose of sintering: The PTFE particles are fused and bonded at high temperature to form a dense structure.
Key parameters:
- Temperature: 360-380 ° C (below melting point 327 ° C can not be completely melted, above 380 ° C is easy to decompose).
- Heating rate: Slow heating (1-2℃/min) to avoid cracking caused by temperature difference between inside and outside.
- Holding time: Depending on thickness (usually 1-2 hours /10mm thickness).
- Cooling rate: natural cooling or controlled cooling (too fast cooling is easy to produce internal stress).

