Contamination injection molding is one of the most common yet often overlooked challenges in plastic manufacturing. Left unchecked, it can lead to various injection molding defects, disrupt production efficiency, compromise part quality, and increase overall costs. Gaining a clear understanding of its causes and effective prevention methods is key to ensuring consistent, high-quality results.
Why Focus on Injection Molding Contamination?
Contamination injection molding introduces foreign particulates, such as dust, grease, or incompatible polymers, into the production process, thereby compromising the quality of molded components. These impurities precipitate a cascade of issues, including aesthetic defects, diminished mechanical properties that lead to part failure, and elevated production costs due to increased scrap rates and rework. Moreover, failing to control contamination risks results in goods that do not meet regulatory or client specifications, potentially leading to contractual penalties or a loss of reputation.
Common contamination defects in injection molding include splay (streak-like discolorations caused by moisture), delamination (layer separation because of incompatible materials or moisture), black spots or dark inclusions from dirt or degraded materials, and surface blemishes from mold residue or improper lubrication.
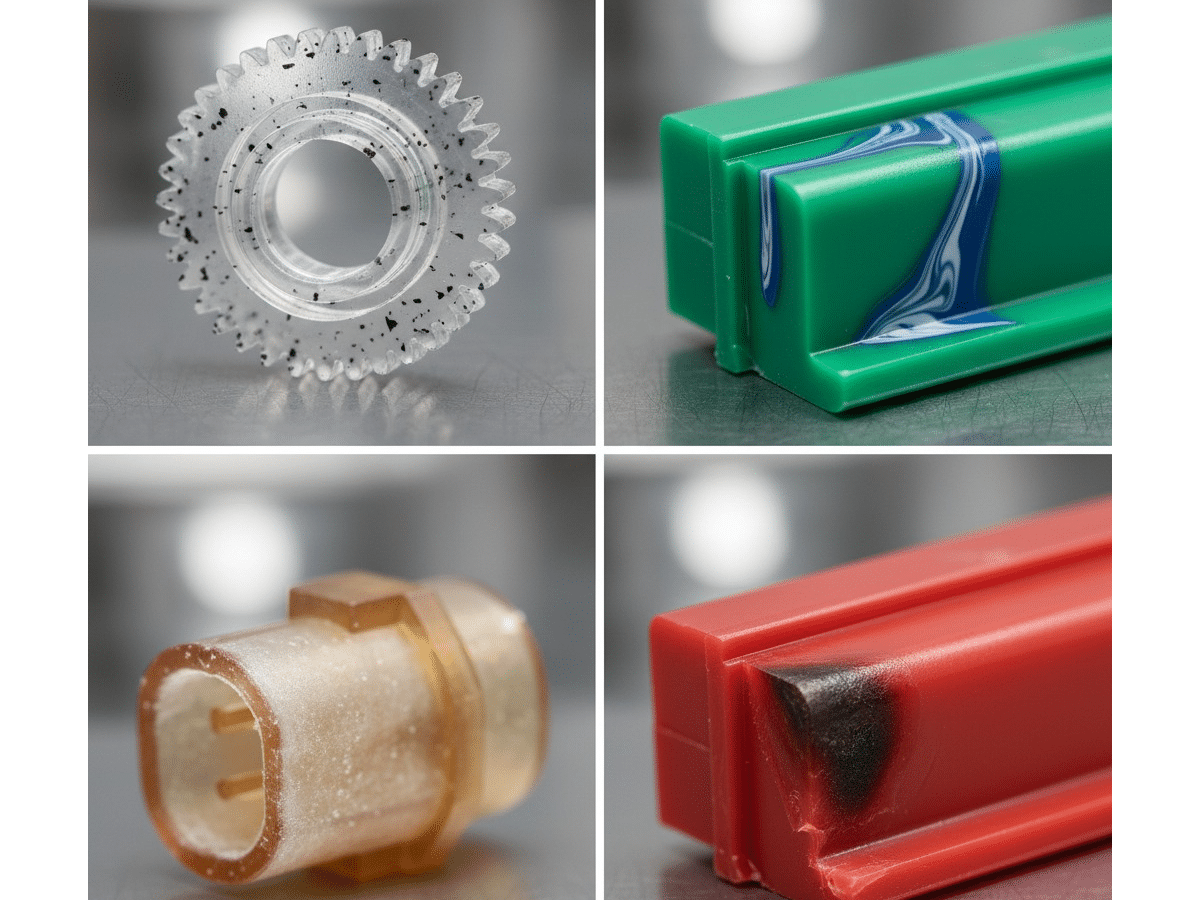
Common Sources of Contamination Injection Molding
Contamination in injection molding originates from multiple sources. Identifying and addressing these sources is important to ensuring defect-free components.
Raw Materials
Raw materials form the foundation of the injection molding process, and any contamination here directly compromises product quality. Contaminated raw materials can include degraded pellets, foreign particles, or improper regrind mixing.
Moisture is another significant contaminant; plastic resins and fillers can absorb water, resulting in steam formation during molding that creates defects like splay.
Poor storage conditions, such as exposure to dust or humidity, also elevate contamination risks.
Machines and Screws
Injection molding machines, particularly their barrels and screws, are prone to contamination from residual materials left by previous production runs. These residues, if not purged, mingle with new material, causing discoloration, burn marks, or inconsistent material flow.
Degraded polymers within the barrel, subjected to repeated heating cycles, further compound the problem, introducing volatile contaminants.
Mold Surfaces
The mold itself, a critical component in shaping parts, is a prime site for contamination. Grease, rust, or residual mold release agents on mold surfaces can transfer to the molded part, resulting in surface imperfections or poor part release. These contaminants not only affect aesthetics but can also impair functionality.
Human Error
Improper handling of raw materials, such as exposing resins to open air or failing to follow cleaning protocols, invites dust, moisture, or other particulates into the process. Inadequate training or lapses in workshop discipline further amplify risks.
How to Avoid Contamination in Injection Molding?
Preventing contamination in injection molding demands a multifaceted approach. Here are the best practices of each stage of the process.
Material Handling
Store materials in sealed containers away from dust, dirt, and moisture. Before molding, dry all hygroscopic materials according to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure moisture content is within acceptable limits. Employ clean transfer methods, avoid mixing regrind with virgin material without proper checks, and keep granulators thoroughly cleaned between material changes to prevent cross-contamination.
Machine Maintenance and Cleaning
Purging barrels and screws with specialized cleaning compounds removes residual polymers and degraded materials, preventing cross-contamination between runs. Scheduled maintenance checks, including inspection of heating elements and material feed systems, help identify potential sources of contamination. Automated cleaning systems enhance efficiency by reducing downtime while ensuring thorough decontamination.
Mold Cleaning and Coatings
Maintain molds by cleaning them frequently to remove any residue buildup, contaminants, or excess lubricant. Avoid excessive use of mold release sprays and lubricants. Use only optimized quantities tailored for the specific mold and material. Consider applying specialized mold coatings designed to resist contaminant adhesion and improve mold release properties.
Workshop Management
Implement strict housekeeping protocols, regular floor and equipment cleaning, and waste removal strategies to minimize dust and debris accumulation. Train operators and maintenance staff on contamination risks and mitigation procedures, emphasizing the importance of their role in preserving product integrity. Consider automation and robotic handling in areas prone to contamination to reduce human contact.
Choosing Jingzhi as Your Injection Molding Supplier
While contamination in injection molding can lead to numerous quality defects, these challenges can be avoided when partnering with an experienced and professional injection molding manufacturer. Jiangzhi is a professional injection molding manufacturer. Our comprehensive contamination prevention strategies encompass every stage, enabling Jingzhi to consistently manufacture parts that meet the highest quality standards with minimal defects.