Custom Plastic Parts
Explore our capabilities and learn how we bring your custom plastic components to life through material selection, plastic fabrication, and custom molding.
- Rapid prototyping with fast delivery
- Complex geometries and tight tolerances
- Smooth surface finishes and custom textures
- Expert mold design and manufacturing

Plastic is a lightweight, durable material that can be molded into complex shapes while offering strong insulation and resistance to wear and corrosion. It’s widely used in industries like automotive, toys, and packaging, and often replaces metal or rubber when strength and design flexibility are needed.
Custom plastic parts are tailored components made to meet specific design or functional requirements. At Jiangzhi, we offer a full range of manufacturing processes such as injection molding, compression molding, overmolding, insert molding, extrusion, and CNC machining. With years of plastic parts Manufacturing experience and technical expertise, we deliver high-quality solutions you can rely on.
Custom Molded Plastic Parts Manufacturing Methods
Click to View
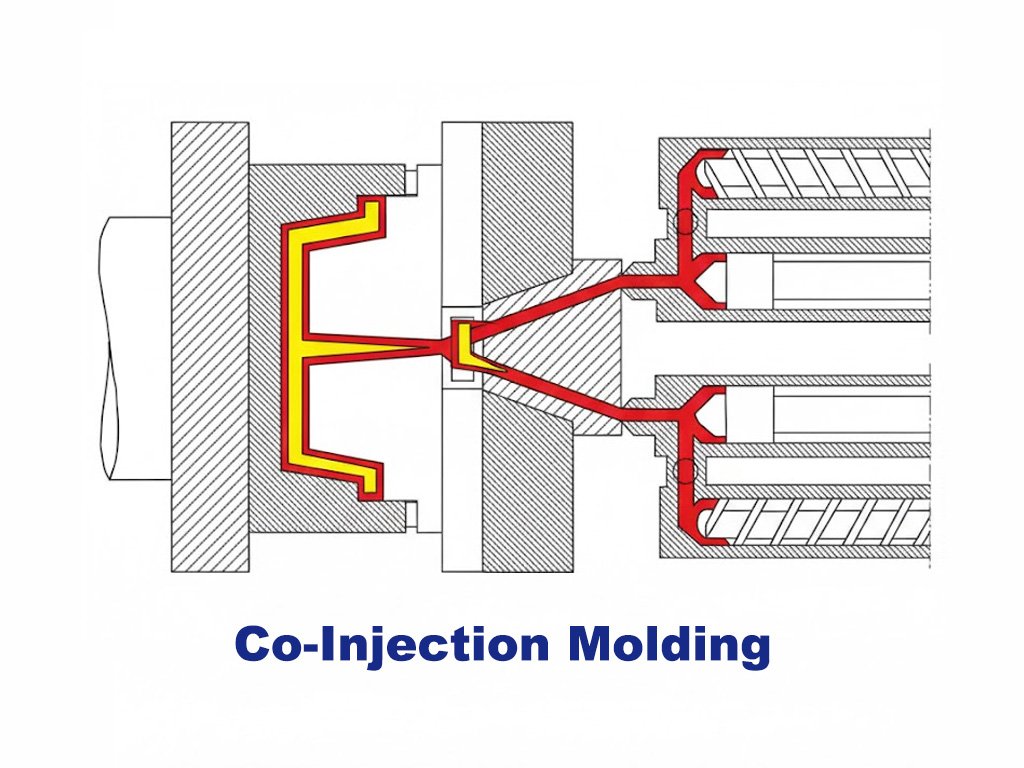
Plastic Injection Molding
Custom Plastic injection moulding is one of the most common and efficient methods for producing custom plastic parts. In this process, molten plastic is injected into a closed mold under high pressure, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. It is ideal for high-volume production and for creating parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
This method is particularly well-suited for producing small-to-medium-sized plastic parts with intricate details, thin walls, or multiple features. It supports a wide range of thermoplastics materials.
Advantages:
- Highly efficient for large-scale production with low per-unit cost at high volumes.
- Capable of producing parts with complex geometries and fine details.
- Excellent repeatability and consistency between parts.
- Supports a wide variety of plastic materials and color options.
Disadvantages:
- High initial tooling cost and longer lead time for mold manufacturing.
- Design changes after mold creation can be costly.
- Not economical for small production runs.
- Waste from runners and sprues may require recycling.
CNC Plastic Machining
Machined plastic parts use computer-controlled cutting tools to remove material from a solid block of plastic to create precise shapes. It is ideal for producing prototypes, small to medium production runs, and custom plastic parts with tight tolerances.
This process is particularly well-suited for plastic components that require exceptional dimensional accuracy, complex contours, or specialized engineering plastics that may be difficult to mold.
Advantages:
- No expensive molds required, making it cost-effective for low-volume production.
- Excellent precision and surface finish.
- Allows for rapid design changes and prototyping.
- Compatible with a wide range of plastic materials, including high-performance engineering plastics.
Disadvantages:
- Higher material waste compared to molding processes.
- Slower production speed for large quantities.
- Limited ability to produce extremely complex internal geometries.
- Larger parts may require special fixturing or multiple setups.
Plastic Compression Molding
Plastic compression molding involves placing pre-measured plastic material into a heated mold cavity, then closing the mold and applying heat and pressure until the material cures and takes shape. It is ideal for medium-volume production of large, simple parts.
Advantages:
- Lower tooling cost compared to injection molding.
- Well-suited for large and thick parts.
- Can process high-viscosity and fiber-filled materials.
- Minimal material waste with pre-measured charges.
Disadvantages:
- Slower cycle times compared to injection molding.
- Less suitable for highly detailed or intricate designs.
- May require secondary trimming to remove flash.
- More labor-intensive due to manual material loading.
Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process where molten plastic is forced through a shaped die to create products with a consistent cross-section, such as pipes, tubes, and profiles. It is ideal for producing long, uniform parts in high volumes.
This process works best for simple, continuous shapes and is widely used in industries like construction, automotive, and packaging.
Advantages:
- Highly efficient for continuous, large-scale production.
- Low tooling cost compared to molding processes.
- It can produce very long parts with uniform profiles.
- Supports a variety of thermoplastics and additives.
Disadvantages:
- Limited to products with a constant cross-sectional shape.
- Post-processing (cutting, cooling, surface finishing) may be required.
- Dimensional precision can be affected by cooling rates and material shrinkage.
- Not suitable for complex or closed hollow structures without additional processes.
Need Custom Plastic Components? Let’s Build Them Together.

Material Options for Molded Plastic Components
Plastic materials vary in properties and processing needs. We help you choose the best fit for your application and budget. Common molded plastic materials include:
- ABS
- PC
- PP
- POM
- PE
- PS
- PVC
- PTFE
- PU
- PA
- PMMA
Applications of Custom Plastic Parts
Custom plastic components are used across a wide range of industries. Common applications include:
- Plastic housings
- Plastic gears
- Plastic brackets
- Fabricated plastic panels
- CNC plastic components
- Custom molded plastic parts
- Custom plastic pulleys
- Plastic handles
- Plastic knobs
- Custom plastic connectors
- Custom plastic seals
- Custom plastic rollers
How to Work with Us?
Upload a CAD File
Quote & Design Analysis
Manufacturing Begins
Parts Shipped
On-Time
One-Stop Custom Plastic Parts Manufacturer
We offer end-to-end plastic manufacturing service solutions, from prototype to high-volume production, ensuring consistent quality and responsive service.