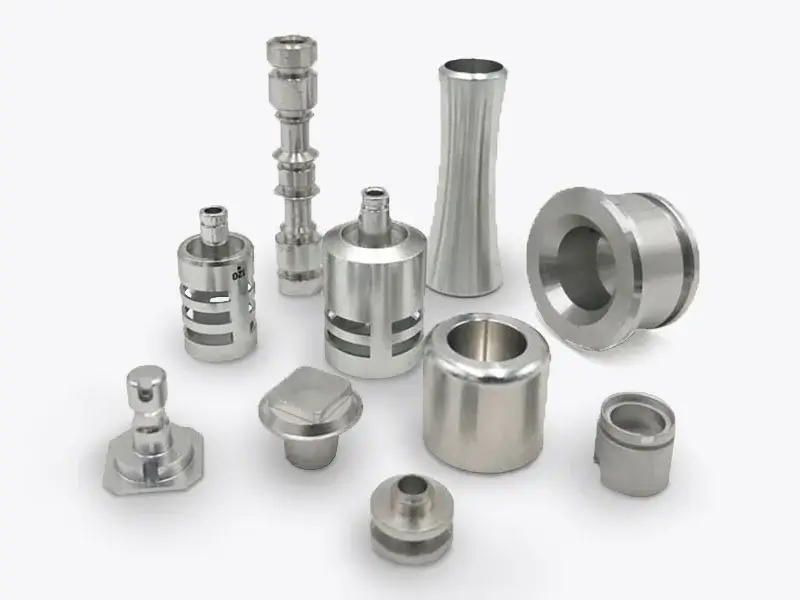
CNC turning parts can meet tight tolerances and complex geometries. In this article, we will learn the CNC turning process, CNC turning parts, and design tips.
What is CNC Turning and How Does It Work?
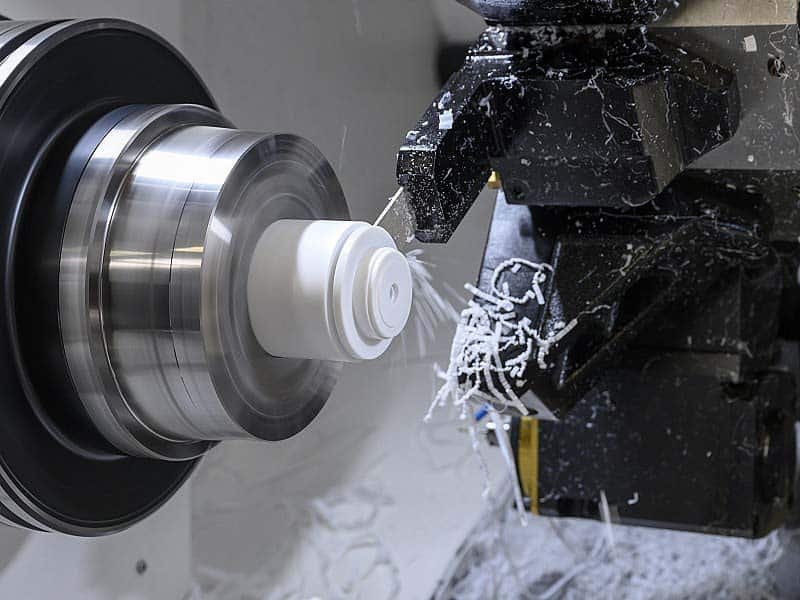
Precision CNC turning is a subtractive manufacturing process that shapes a rotating workpiece using a stationary cutting tool, typically performed on a CNC lathe machine. The process excels at creating cylindrical or axially symmetric CNC turned components, such as shafts, pins, and threaded parts. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes rely on advanced software to ensure precision and repeatability.
The process begins with a 3D CAD model of the desired part. This model is converted into G-code, a programming language that directs the lathe’s movements. The workpiece, secured in a chuck or spindle, rotates at high speeds—often thousands of RPM—while a single-point cutting tool removes material to achieve the programmed geometry. Operations include facing, threading, drilling, grooving, and knurling, producing intricate CNC lathe components with tight tolerances.

Material Selection for CNC Turned Parts
The choice of material for CNC lathe machining parts is critical, as it influences machinability, durability, and application suitability. Common materials include:
Metals for CNC Turned Parts
- Aluminum: Lightweight and machinable, ideal for automotive CNC lathe components like brackets and housings.
- Steel and Stainless Steel: Durable and corrosion-resistant, used for industrial parts of CNC lathe applications, such as gears and shafts.
- Brass: Conductive and aesthetically pleasing, perfect for electrical connectors.
- Titanium: High-strength and lightweight, favored for aerospace CNC turned components like turbine blades.
- Copper: Excellent for thermal conductivity in electronics fittings.
Plastics for CCNTurnedParts
- ABS: Impact-resistant, used for consumer goods.
- Nylon: Wear-resistant, suitable for bearings and bushings.
- PEEK: High-performance plastic for medical CNC turning parts, such as implants.
- Polycarbonate: Transparent and durable, ideal for optical components.
Advantages of CNC Turning Parts
CNC turned components provide benefits that make them indispensable in manufacturing:
Precision and Accuracy
The CNC lathe machine components and software enable precision down to microns, ensuring each part aligns with strict tolerances.
Consistency and Efficiency in Production
Automated programs produce identical parts across thousands of units, crucial for mass production.
Complex Geometry Capability
CNC turning can create intricate features such as threaded holes, grooves, and flanges on round parts with ease.
Material Efficiency
By working from bar or tube stock, CNC turning minimizes material waste compared to other subtractive techniques.
Speed and Productivity
CNC lathe machining parts are produced swiftly with minimal setup time, benefiting high-volume manufacturing.
Integration of Secondary Operations
Live tooling and multi-axis capabilities enable drilling, milling, and tapping without part transfer, reducing lead times.
Types of CNC Turning Parts Application
CNC turning parts have rotational symmetry and cylindrical or conical shapes. They are made from diverse materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper, titanium alloys, and engineering plastics. CNC turning is ideally suited for high-precision, efficient mass production of complex cylindrical or tapered parts, with broad applications across automotive, aerospace, medical, and machinery industries.
Shaft parts: including rotating shafts, drive shafts, and transmission rods, are widely used in mechanical transmission systems.
Pin parts: such as locating pins, connector pins, and dowel pins.
Sleeve parts: including bushings, shaft sleeves, and bearing rings.
Valve parts: valve bodies, valve cores, valve seats, and valve stems are commonly used in fluid control systems.
Gear parts: small gears, worm gears, and similar components.
Flanges and connectors: various flange plates and pipe connectors.
Threaded parts: bolts, nuts, and screws.
Medical instrument parts: components for surgical instruments and implants requiring high precision.
Aerospace parts: turbine shafts, jet engine components, etc.
Automotive parts: crankshafts, camshafts, piston pins, drive shaft sleeves, etc.
Electronic components: terminals, plugs, and sockets.
Precision machinery parts: pump bodies, valve bodies, and instrument components.
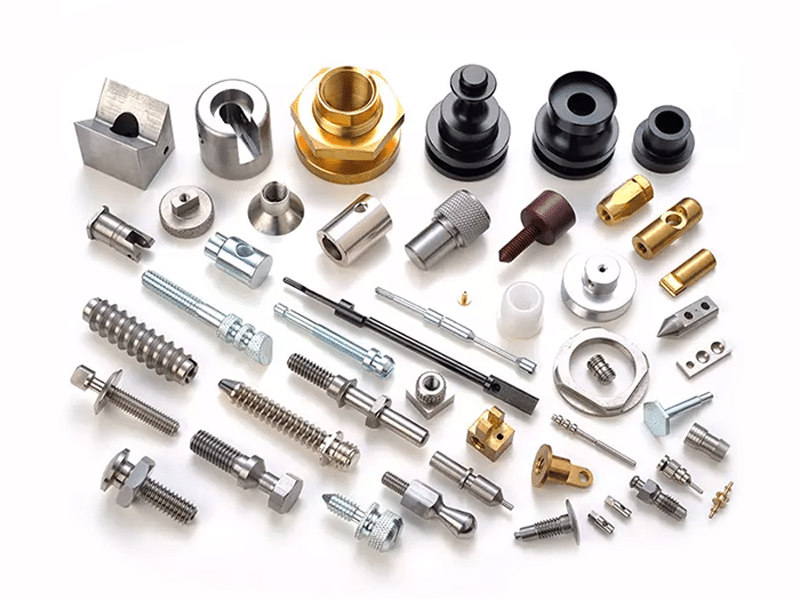
Best Practices for CNC Turning Design
Designing for CNC turning requires foresight to ensure manufacturability and cost-effectiveness. Key best practices include optimizing for tool accessibility, using standard feature sizes, minimizing secondary operations, and designing short, robust parts to reduce deflection. Incorporating radii or chamfers instead of sharp corners and adding thread reliefs prevents burrs and simplifies machining. These principles streamline production and enhance the quality of CNC plastic parts.
High-Quality CNC Turned Components Service
High-quality CNC turned components are defined not only by tight dimensional tolerances but also by superior surface finishes, material integrity, and functional reliability. At Jiangzhi, high precision turning is achieved through a combination of modern equipment, skilled engineers, and rigorous quality control processes. The ability to handle various materials, from metals to engineering plastics and complex geometries. Welcome to contact Jiangzhi for a custom CNC turning service.





