When developing custom plastic components, two of the most common methods are injection molding and vacuum forming. Both processes are used to produce plastic parts, but they have distinct advantages and limitations depending on the project requirements. This article will compare injection molding and vacuum forming in terms of their definitions, advantages, process capabilities, and factors to consider when choosing the right method for your project.
What Is Injection Molding?
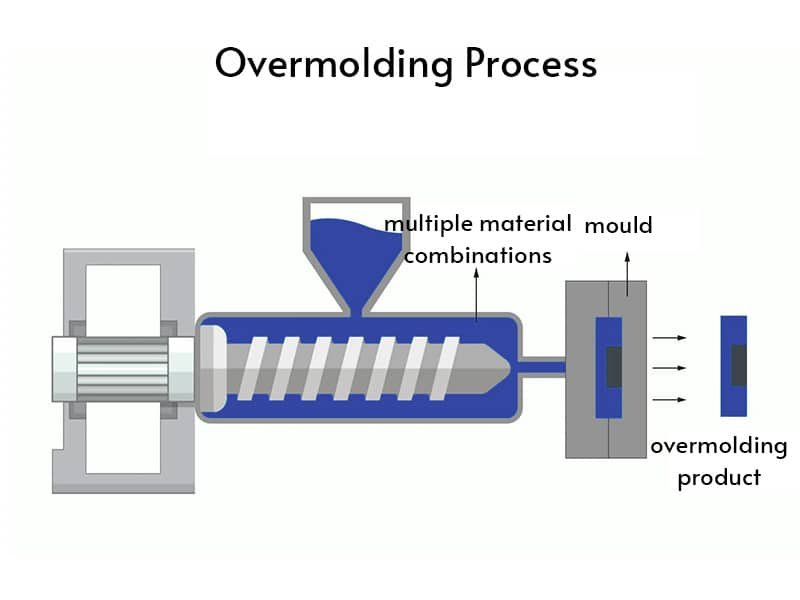
Injection molding service is a manufacturing process in which molten polymer is forced under high pressure into a closed metal mold. Plastic material is fed into a heated barrel, melted by a reciprocating screw, and then injected at high pressure. The mold remains clamped shut while cooling channels remove heat, solidifying the part in a short time. Ejector pins then push the finished component out of the mold.
Injection molding is particularly well-suited for large-scale production runs. It is capable of producing intricate and detailed parts, such as gears, enclosures, and components with integrated features like threads or bosses.
Advantages of Injection Molding
- High Precision and Consistency: Injection molding can produce parts with very tight tolerances, ensuring that each part is identical in size and shape.
- Complex Designs: Injection molding supports the production of complex parts with intricate features, including fine threads, undercuts, snap-fits, living hinges, and multi-material components.
- Material Variety: A wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets can be used in injection molding. This allows more flexibility in choosing materials.
- Automation and High Volume Runs: Injection molding is a highly automated process. It is cost-effective for large-volume production.
What is Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming is a type of thermoforming. It is a simpler process compared to injection molding. In vacuum forming, a thin sheet of plastic is heated until it becomes pliable. This sheet is then draped over a mold, and a vacuum is applied to remove the air between the mold and the sheet. The vacuum forces the sheet to conform to the shape of the mold. Once the material cools, the part is removed, and excess material is trimmed away.
Vacuum forming is ideal for producing larger parts with simple geometries. It is commonly used in industries such as packaging, automotive, and signage, where large panels, covers, or packaging components are needed.
Advantages of Vacuum Forming
Cost-Effective for Low to Medium Volumes: Vacuum-forming molds are simpler and less expensive. It is more cost-effective for lower production runs or prototype parts.
- Large Part Sizes: Vacuum forming is well-suited for larger parts, as the molds do not require the same complex design elements as injection molds.
- Faster Turnaround Time: Mold fabrication is faster than injection molding, allowing quicker prototyping and shorter production timelines.
- Easier and Cheaper to Modify: Since vacuum forming molds are simpler, they are also easier and more cost-effective to modify.
Comparison of Injection Molding vs Vacuum Forming
| Feature | Injection Molding | Vacuum Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Process | High-pressure injection into closed two-part mold | Heated sheet drawn over single-sided mold by vacuum |
| Precision and Tolerances | High precision and tight tolerances | Moderate precision, suitable for simple shapes |
| Material Options | Broad range, including thermosets and thermoplastics | Limited to thermoplastics |
| Production Volume | Best for high-volume production runs | Best for low to medium-volume production |
| Mold Cost | High initial tooling cost, especially for complex parts | Lower tooling cost, good for prototypes |
| Mold Material | P20 Steel | Part Size |
| General Tolerance | Best for small to medium-sized parts | Suitable for larger parts with simpler geometries |
| Cycle Time | Short cycle time for high-volume production | Longer cycle time for each part due to the heating and cooling process |
| Typical Lead Time | 12–20 weeks for production mold | 2–8 weeks for production tool |
| Design Flexibility | High flexibility for complex shapes and multiple features | Limited to simple shapes and single-layer designs |
| Common Applications | Medical devices, electronics housings, automotive connectors, consumer goods | Trays, enclosures, panels, signage, vehicle interiors, refrigerator liners |
When to Choose Injection Molding or Vacuum Forming?
What factors should you consider when you need to customize injection molding or vacuum forming?
- Production Volume: Injection molding becomes more cost-effective at higher production volumes due to its ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly. If you need to produce thousands or millions of parts, injection molding is likely the better choice.
- Part Complexity: If your design includes intricate features, such as internal threads, undercuts, or fine details, injection molding is the clear choice. It is also better suited for parts that require high precision. Simple, shallow geometries with large surface area favor vacuum forming.
- Material Requirements: If your part requires a material that needs to withstand extreme temperatures, chemicals, or other specialized conditions, injection molding offers a wider range of materials. Vacuum forming is limited to thermoplastics.
- Cost and Lead Time: If your project involves a lower production volume or requires fast prototyping, vacuum forming may be a more economical option. The tooling costs for vacuum forming are significantly lower, and the production lead times are shorter.
- Part Size: For large components, vacuum forming is often the preferred method. It can accommodate larger parts with simpler geometries, such as trays, covers, and panels, that are often used in packaging and automotive industries.
Conclusion
Both injection molding and vacuum forming are highly effective plastic manufacturing methods, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. They are complementary rather than competing technologies. Ultimately, the choice between injection molding and vacuum forming depends on the specific needs of your project, including part complexity, production volume, material choice, and budget. Welcome to contact Jiangzhi, who provides on-demand manufacturing and professional custom solutions for your plastic parts project.